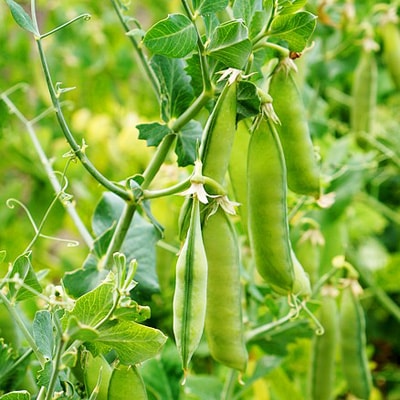
This is an annual legume with an erect or climbing stem from 45 to 250 cm long. Serves as a rich source of protein and various amino acids. It is quite unpretentious, produces good yields and is widely used for culinary needs, as it is nutritious, well digestible and has excellent taste.
General information about vegetable peas
These peas come in two varieties: shelling and sugar. The first has a rough parchment layer inside the bean, so only the grains remaining after peeling are eaten. The sugar variety is eaten whole, on a blade or in the form of green peas. The shells of such peas are fleshy, juicy, and edible. The grains themselves can be round, smooth or wrinkled (brain varieties).
A number of important advantages make this crop very popular and often grown. Peas:
- cold resistant;
- tolerates excess moisture well;
- resistant to short-term droughts;
- has a powerful branched root system;
- undemanding to predecessors.
The plant can withstand low ambient temperatures down to −4 C. Round, smooth varieties of seeds best resist frost. Their germination occurs at a slight positive temperature of 1-2 °C, and for brain varieties – at 4-8 °C. At a temperature of +16-20 °C, the best conditions are created for seed germination and growth of the finished plant.
Moisture is especially needed by peas during seed germination at the beginning of the growing season. Excessive soil moisture is not harmful to the plant, but high groundwater can be detrimental to it. The most suitable humidity would be 75-80% of the total field moisture capacity – FPV.
At the same time, short-term droughts can be tolerated by plants well due to a powerful, well-developed root system, which allows them to extract water from deeper layers of the soil.
Soil preparation and planting
The most suitable soil for peas is light loamy and sandy loam soils, previously well cultivated and fertilized. It is also possible to grow a crop of this crop on heavy and drained soils, but there the peas are more suppressed and it is impossible to obtain the maximum possible yield.
Vegetable peas can be preceded by any crops, but the best solution is tomatoes, cucumbers, potatoes, and cabbage.Moreover, applying fertilizers in the form of manure for these crops will subsequently be very useful for peas.
Peas cannot be planted in depleted, acidic and saline soils; soils with high groundwater levels are also not suitable. In the fall, it is good to prepare the soil for planting: destroy the plant remains of predecessors, weeds, and use deep autumn plowing or digging to a depth of 22-25 cm.
Peas must be planted in a well-lit, sunny, unshaded field in sufficiently moist soil. It is advisable to plant in several stages, with seeds of different varieties, with different ripening periods. The usual sowing time in Ukraine is the end of April – the end of May.
The most commonly used planting pattern is a two-line ribbon: 50 cm between ribbons and 20 cm between lines for peeling varieties, 40 cm for sugar varieties. In a row, plants should have an interval of 4-6 cm and a sowing depth of 3-4 cm for heavy soils, 5-6 for light soils. After sowing, it is very good to compact the soil above the seeds to prevent birds from pecking.
Timely watering is extremely important for this crop, especially during the period of seed germination and emergence, as well as weeding, loosening the soil and destroying pests. Water the peas once a week or more often, at the rate of 8-10 liters per square meter. m.
In addition, fertilizing with mineral fertilizers – urea, superphosphate – is necessary during flowering. It is convenient to combine this fertilizing with the next watering by dissolving fertilizers in water for irrigation (10-20 grams per sq. m.)
Cultivation and harvesting
Peas ripen in early summer, and the first harvest is already harvested in June. Harvesting is carried out several times, as beans of different varieties, planted at different times, ripen.
Hulling varieties for producing green peas are harvested when the grains reach their maximum size in the pod and green leaves form, before a net forms on them. Sugar beans are harvested when they reach maximum meatiness, tenderness and juiciness.
The pea crop of all varieties is used in the following types:
- fresh;
- canned;
- dry;
- frozen;
- in soup;
- for garnish;
- to salad.