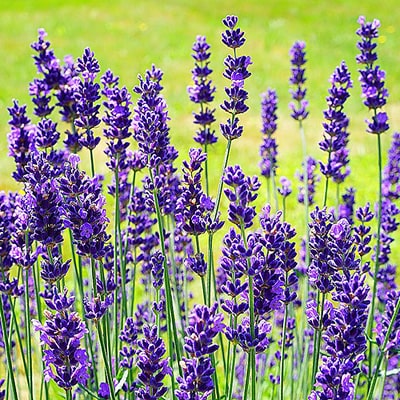
Lavender – what kind of plant is this?
This is a perennial crop of the Lamiaceae family. Initially it grew naturally in Africa, Asia, and southern Europe. Thanks to its beneficial properties, beautiful flowers and strong pleasant aroma, it is now widespread: grown in fields, gardens and front gardens around the world. There are approximately 25-30 different species of this plant.
Under natural conditions, this is a heat-loving, southern crop, but currently it is successfully grown in colder climates, on dry soils. Our gardeners willingly plant lavender in their summer cottages, where it safely withstands the winter cold. Many cold-resistant varieties have been developed that are grown from seeds as an annual plant.
In especially cold climatic zones, lavender is grown in special portable flowerpots, which, with the onset of cold weather, are transferred to a warm room – a house or a winter garden.
Lavender is a very useful, widely used plant, so it is planted and cultivated on an industrial scale. In Europe, for example, the huge lavender fields of the province of Provence are famous. In our area, this crop is grown everywhere in the Crimea, as well as in many regions of Russia, Ukraine, Moldova, and even in Altai and the Urals, in Siberia.
Features of planting, care, and watering lavender
To successfully grow this crop, the following parameters must be observed:
- location;
- soil;
- watering;
- wintering;
- cropping;
- collection.
The plant loves an abundance of light and warmth, even the sun is suitable, but lavender simply does not grow in the shade. The soil must be saturated with oxygen and potassium, but in general the crop is not at all demanding on soil. Light loamy and sandy loam, loose, calcareous soil is good. Poor, infertile soils are also suitable.
Lavender does not tolerate high humidity; excessive watering will be destructive for it. It is better not to water the plant at all than to overwater it. Natural moisture obtained from dew and rain is sufficient.
A successful winter is also directly related to the absence of excess moisture. Thus, plants located on a high, dry area will withstand even a frosty winter much better than bushes in a low flowerbed that are susceptible to damping off. Alternating frosts and thaws and spring excess moisture also have a very bad effect. Mulching with loose dry peat or leaf humus helps well during wintering.
Pruning of shoots is carried out when flowers are collected, at the peak of their flowering. You can cut them off with part of the shoot, forming beautiful round bushes. In spring, the tops are sometimes trimmed, but this is not a necessary operation. From time to time, unscheduled pruning is carried out to rejuvenate the bushes. They are made quite high, without capturing woody shoots, otherwise the plant may die.
At the height of lavender’s flowering, its flowers are collected and dried in a shaded and ventilated room. For collection, you should choose the time of the most intense flowering, when the color and aroma gain maximum strength.
How to propagate lavender?
The most common methods of propagation of this plant are as follows:
- planting seeds;
- dividing a bush;
- layings;
- cuttings.
The seed, after stratification for 30-40 days, subject to a temperature regime of +5 ° C, is sown on seedlings, which are then transplanted to a permanent place.The division of the bush is carried out in the fall, when old plants grow and produce many shoots and lateral roots. Layerings and cuttings produce several shoots suitable for rooting.
Growing lavender can be a very profitable business – the harvest of this crop is in demand, and the demand is quite high. Caring for plants is simple and does not require large expenses. You can start growing lavender in a small area of 1-2 hectares or even half a hectare. Lavender has no natural enemies – pests, fungi and insects, as they are repelled by the aroma of the plant itself.
The most important thing is to choose a dry area without excess moisture, well lit by sunlight. Young plants in dry climates can be watered, but very carefully, without giving excess moisture. In this case, drip irrigation is very good – it guarantees the absence of waterlogging.
Weed control is also important. Weeding must be done at least 5-6 times during the flowering season, manually or mechanically. Chemical treatment is prohibited – plant flowers are used in production for food and cosmetic purposes, and the crop treated with chemicals will simply be rejected by the buyer.
It should be noted that the second lavender harvest is harvested at the end of summer. The yield of the crop is 50-70 centners of flowers per hectare, and this is up to 90 kg of essential lavender oil. With an average wholesale price per liter of about 50 euros, and a retail price of 80 euros, such a business can be considered very profitable.
Why is lavender grown?
The scope of this culture is extremely wide. It is used:
- for the production of cosmetics and perfumes;
- in medicine;
- in cooking;
- for decorative cultivation;
- for household use.
Lavender oil is especially valued. There are many varieties of perfumes and other flavorings, where the percentage of its addition varies to obtain different aromas. Aromatic fragrances are added to washing powders, detergents, deodorants and other cosmetic products. The strong, long-lasting, elegant scent of lavender is extremely popular among men and women of all ages.
Doctors value the antiseptic, antibacterial and antispasmodic properties of lavender oil. It is used as a medicine, as well as in aromatherapy – for various baths, spa treatments, and massage. Aroma lamps are successfully used in beauty salons and at home.
The dried flowers of the plant are widely used in cooking. These are spices for various dishes, drinks, desserts. During the flowering season, fresh plants are also used for these purposes.
In addition to industrial cultivation, lavender is readily planted in gardens and summer cottages. Its purple flowers create a magnificent interior, serve as a living border, and scent the air. But in addition to decorative decoration, these plants perfectly serve as protection for garden plantings from the Colorado potato beetle and rodents.
Many housewives like to keep dried bunches of lavender in their apartments and houses. This is a wonderful natural flavoring agent, as well as an excellent remedy for repelling household pests such as mice and moths.